Shin splints, medically known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are a common affliction among runners, athletes, and individuals engaged in high-impact activities.
This painful condition, marked by discomfort along the shinbone (tibia), can significantly impact one’s ability to train and perform optimally.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of shin splints, exploring its definition, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis.
1. What is Shin Splints?
Shin splints refer to the inflammation of the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue surrounding the tibia.
It typically occurs as a result of repetitive stress, overuse, or sudden increases in physical activity.
Runners, dancers, military recruits, and individuals participating in activities involving repetitive jumping or running are particularly susceptible to this condition.
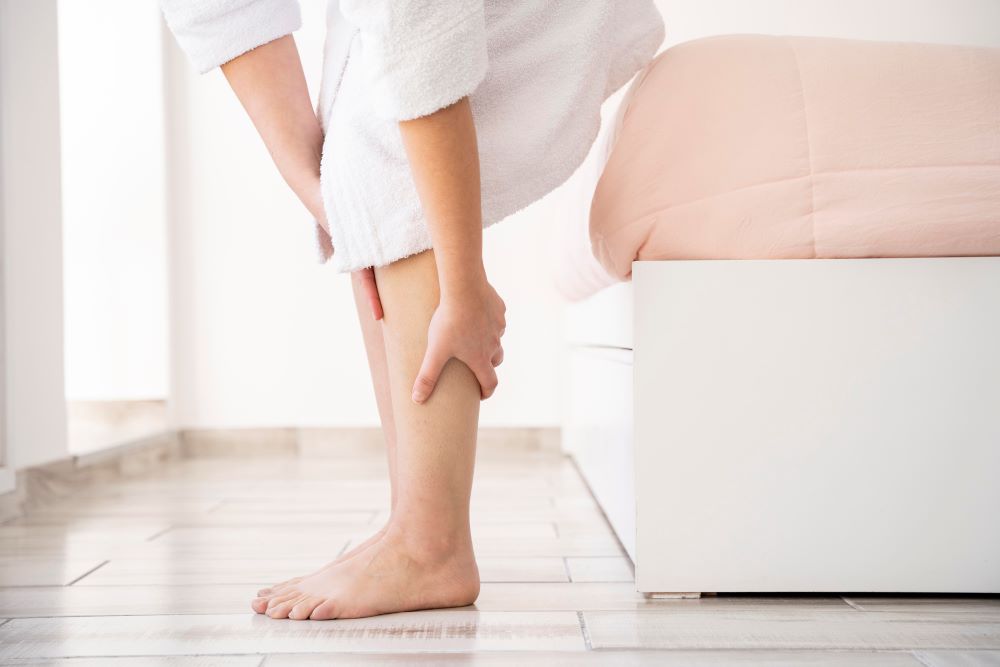

2. Symptoms
Common symptoms of shin splints include:
- Dull, aching pain along the inner aspect of the shinbone.
- Tenderness, soreness, or swelling in the affected area.
- Pain that worsens during physical activity and may persist after exercise.
- Discomfort when pressing on the affected area.
3. Cause
Several factors contribute to the development of shin splints, including:
- Overuse: Engaging in high-impact activities without proper rest and recovery.
- Muscle Imbalance: Weakness or tightness in the muscles of the lower leg, particularly the calves and shins.
- Improper Footwear: Inadequate support or worn-out shoes can exacerbate stress on the lower leg.
- Training Errors: Sudden increases in mileage, intensity, or changes in running surface.
- Biomechanical Issues: Overpronation, flat feet, or high arches can alter the mechanics of the lower limb.
Research studies have indicated that athletes, military personnel, and individuals involved in activities with repetitive pounding on hard surfaces are at increased risk of developing shin splints.
Moreover, beginners or those returning to exercise after a period of inactivity may also be susceptible.
4. Diagnosis of Shin Splint
Diagnosing shin splints typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to rule out other potential causes of pain.
Physicians may also perform tests to assess muscle strength, flexibility, and biomechanics of the lower limb.
5. Treatment options
How to treat shin splints? Treatment strategies for shin splints focus on reducing pain, inflammation, and addressing underlying contributing factors. Common interventions include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Temporary cessation of high-impact activities to allow for healing.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen may help manage pain and swelling.
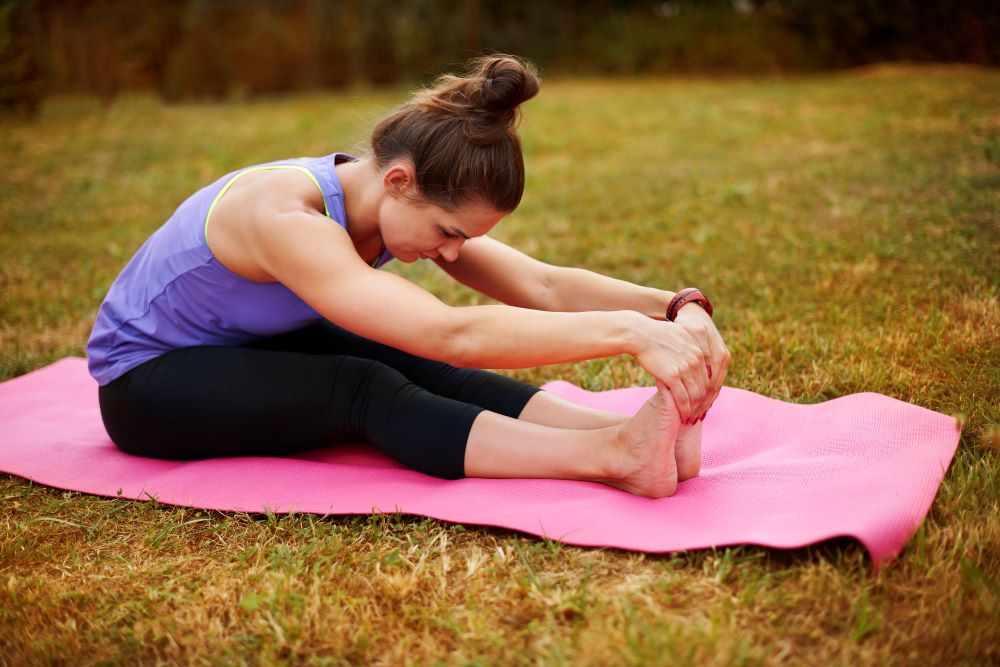
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises to improve muscle balance, flexibility, and biomechanics. Here are our 10 recommended self-exercises to improve your shin splints.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotics or shoe inserts to provide support and correct biomechanical abnormalities.
- Gradual Return to Activity: Progressive reintroduction of exercise once symptoms subside, with emphasis on proper technique and gradual increases in intensity.
6. Prognosis of Shin Splint
With appropriate treatment and adherence to preventive measures, the prognosis for shin splints is generally favorable.
Most individuals experience significant improvement within a few weeks to months with conservative management.
However, failure to address underlying causes or premature return to activity can lead to chronic or recurrent symptoms, necessitating more aggressive interventions.
7. Conclusion
Shin splints represent a common and often frustrating condition that affects individuals of all ages and fitness levels.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for shin splints, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate their risk and promote optimal musculoskeletal health.
Early recognition, appropriate intervention, and adherence to preventive measures are essential for managing shin splints effectively and minimizing their impact on physical performance and overall well-being.
Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is paramount for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment recommendations tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.

[…] Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, are one of the most prevalent injuries among runners, characterized by pain along the shin bone (tibia). This condition often arises from overuse, improper footwear, or running on hard surfaces. […]