Aromatherapy, derived from the Greek words “aroma” meaning fragrance and “therapy” meaning treatment, has been utilized for centuries across different cultures.
Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, China, and India, where aromatic oils were prized for their therapeutic properties.
In Egypt, aromatic substances were used in religious rituals, cosmetics, and embalming practices.
Meanwhile, in China and India, aromatic plants were incorporated into traditional medicine to treat various ailments and promote healing.
Understanding Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy involves the use of essential oils extracted from plants to improve physical, emotional, and mental well-being.
These oils, often referred to as the “essence” of the plant, contain concentrated compounds that possess distinct therapeutic properties.
Essential oils are extracted from different parts of the plant, including the flowers, leaves, bark, roots, and seeds, through methods such as steam distillation, cold pressing, or solvent extraction.
Each essential oil carries a unique aroma and composition, which determines its therapeutic effects.
The Science Behind Aromatherapy
While aromatherapy is often associated with alternative medicine, its efficacy is supported by scientific research.
Essential oils contain bioactive compounds such as terpenes, phenolics, and esters, which exert physiological effects when inhaled or applied to the skin.
When inhaled, aromatic molecules stimulate olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity, triggering neural signals that affect the limbic system – the part of the brain responsible for emotions, memory, and behavior.
This interaction can evoke emotional responses, promote relaxation, and alleviate stress and anxiety.
Additionally, when applied topically, essential oils can penetrate the skin and enter the bloodstream, where they exert systemic effects on the body.
They possess antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antioxidant properties, making them valuable allies in holistic health and wellness.
Practical Applications of Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy can be administered through various methods, depending on individual preferences and needs. Some common applications include:
- Diffusion: Reed diffusers, ultrasonic diffusers, and nebulizers are popular devices used to disperse essential oils into the air, creating a fragrant and therapeutic atmosphere.
- Topical Application: Essential oils can be diluted in carrier oils and applied to the skin through massage, baths, or compresses, providing localized or systemic relief.
- Inhalation: Steam inhalation involves adding a few drops of essential oil to hot water and inhaling the steam, while direct inhalation involves smelling essential oils from a tissue or inhaler.
- Aromatic Baths: Adding a few drops of essential oil to a warm bath can enhance relaxation and promote overall well-being.
- Personal Care Products: Many skincare, haircare, and hygiene products incorporate essential oils for their aromatic and therapeutic properties.
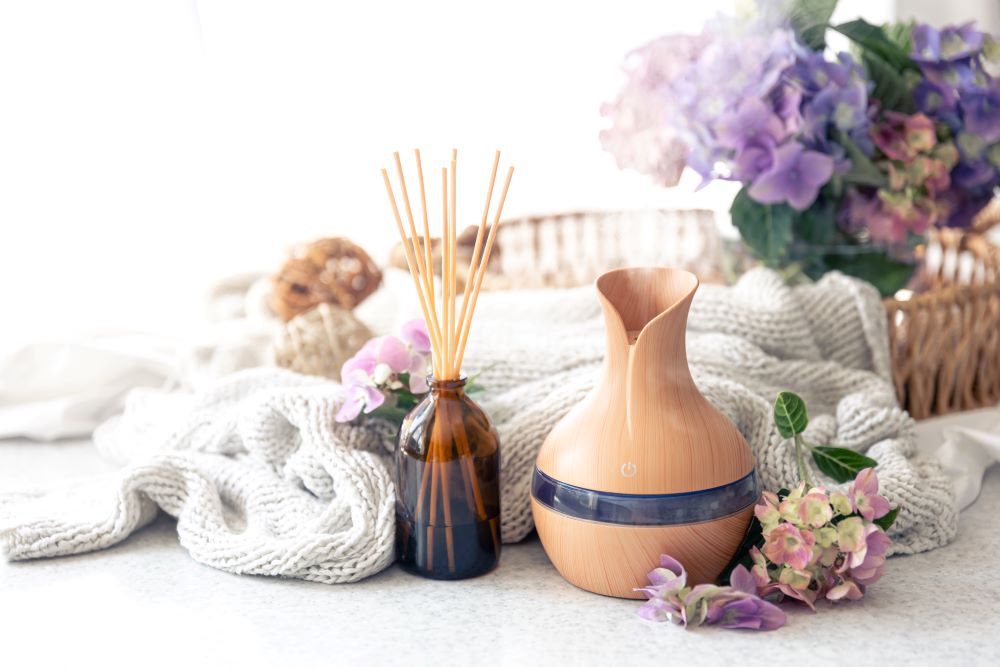

Choosing the Right Essential Oils
With a myriad of essential oils available, selecting the right ones can seem overwhelming.
It’s essential to consider individual preferences, desired effects, and any existing health conditions when choosing essential oils. Some popular essential oils and their therapeutic benefits include:
- Lavender: Known for its calming and relaxing properties, lavender essential oil is often used to alleviate stress, promote sleep, and soothe skin irritations.
- Peppermint: With its refreshing aroma and cooling sensation, peppermint essential oil can help alleviate headaches, improve focus, and relieve muscle tension.
- Eucalyptus: Renowned for its decongestant and invigorating properties, eucalyptus essential oil is commonly used to relieve respiratory symptoms, clear the mind, and promote vitality.
- Chamomile: Chamomile essential oil is prized for its gentle sedative effects, making it ideal for promoting relaxation, easing anxiety, and soothing digestive discomfort.
- Tea Tree: With its potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, tea tree essential oil is effective in treating acne, fungal infections, and minor wounds.
Safety Considerations
While essential oils offer numerous benefits, it’s crucial to use them safely to avoid adverse reactions. Here are some safety considerations to keep in mind:
- Dilution: Essential oils are highly concentrated and should be diluted in a carrier oil before applying to the skin to prevent irritation or sensitization.
- Patch Testing: Before using a new essential oil, perform a patch test by applying a small amount to the skin and observing for any adverse reactions.
- Pregnancy and Children: Some essential oils may not be suitable for pregnant women, infants, or young children. It’s essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional before using essential oils in these populations.
- Sun Sensitivity: Certain essential oils, such as citrus oils, can cause photosensitivity and increase the risk of sunburn. Avoid sun exposure after applying these oils to the skin.
- Quality Matters: Choose high-quality, pure essential oils from reputable suppliers to ensure safety and efficacy.
Conclusion
In a world filled with stress and uncertainty, the therapeutic benefits of aromatherapy offer a beacon of hope and healing.
From promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety to alleviating physical discomfort, essential oils have the power to restore balance and harmony to mind, body, and spirit.
As we continue to explore the wonders of nature’s essence, let us embrace the transformative potential of aromatherapy and embark on a journey of holistic wellness and self-discovery.
Through the simple act of inhaling the fragrant essence of plants, we can unlock the door to a world of serenity, vitality, and renewal.
